Duf3349
- DUF3349 superfamily of proteins:
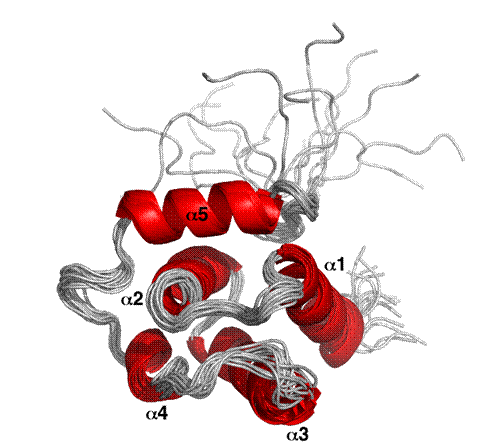
In 2008 approximately 1.6 million people died from the tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Many M.tuberculosis strains are becoming resistant to available antibiotics so a better understanding of the molecular biology of the organism is paramount.Researchers from Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Diseases (SSGCID) have determined the three-dimensional protein structure for Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein Rv0543c, a member of the DUF3349 protein superfamily. This protein is highly conserved in M. tuberculosis and other Mycobacterium and Rhodococcus species and the structure is the first determined for the DIF3349 superfamily. Rv0543c is a 100 residue, 11.3 kDa protein that both size exclusion chromatography and NMR spectroscopy show to be a monomer in solution. As shown in accompanying figure, the structure of the protein consists of a bundle of five α-helices rigidly held together by a largely conserved group of hydrophobic amino acid side chains.
For more information, please see the Protein Data Bank entry 2KVC. This work was published in 2011:
Inaugural structure from the DUF3349 superfamily of proteins, Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0543c. Buchko, G.W., Phan, I., Myler, P.J., Terwilliger, T.C., Kim, C.Y. (2011) Arch Biochem Biophys 506: 150-156 (PubMed: 21144816).