PBGS
- Toxoplasma gondii porphobilinogen synthase (PBGS):
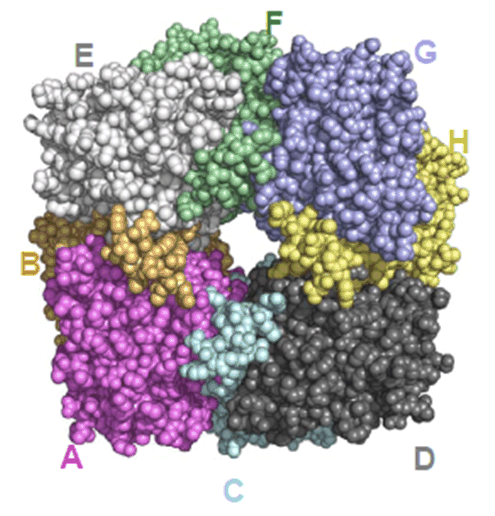
A collaborative effort by a team of researchers from the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Diseases (SSGCID) , Fox Chase Cancer Center and University of Pennsylvania has resulted in the determination of the three-dimensional protein structure of Toxoplasma gondii porphobilinogen synthase (TgPBGS). T. gondii is a protozoan parasite, belonging to phylum apicomplexa, that can infect any warm blooded animal. In humans, although infection in healthy individuals is largely asymptomatic, the parasites can persist as latent cysts for extended periods, sometimes even for the entire life of the affected individual. But infection in pregnant mothers can result in transplacental infection of the fetus resulting in fatal encephalitis and in immunocompromized individuals (due to AIDS, for example) either a new infection by Toxoplasma or recrudescence from an existing latent infection can have fatal consequences. The metalloenzyme PBGS catalyzes an essential step in tetrapyrrole (e.g., heme) biosynthesis in all organisms and has been structurally and biochemically characterized from many different species, including humans. A unique feature of the TgPBGS enzyme is the presence of an extended C-terminal tail region, which is essential for the formation of enzymatically active octameric protein. The crystal structure of TgPBGS reveals how the tail to tail interactions between subunits pairs of dimeric units of TgPBGS facilitate octamer formation. The three-dimensional protein structure of octameric Toxoplasma gondii PBGS is shown. This structure was solved by the SSGCID. As this enzyme is essential for heme biosynthesis in Toxoplasma and is conserved in sequence and function in other apicomplexan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum, the availability of this protein structure will facilitate the development of parasite species specific PBGS inhibitors.
References J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 7. Crystal structure of Toxoplasma gondii porphobilinogen synthase: insights on octameric structure and porphobilinogen formation. Jaffe EK, Shanmugan D, Gardberg A, Dieterich S, Sankaran B, Stewart LJ, Myler PJ, Roos DS.
For more information, please see the Protein Data Bank entry 3OBK.